MIT 6.S191 Introduction to Deep Learning
MIT 6.S191 Introduction to Deep Learning
MIT’s introductory program on deep learning methods with applications in language, medicine, art, computer vision, game play, robotics and more!
Lecture 1: Intro to Deep Learning
Apr. 29, 2024
Deep Learning – The Brainy Robot 🤖🧠
Imagine you have a robot friend who wants to learn how to recognize things, like cats, dogs, or even your handwriting. How does it learn?
Well, we teach it just like a human brain learns! That’s what Deep Learning is all about.
1. The Human Brain vs. Artificial Neural Networks
🧠 Your brain has neurons (tiny brain cells) that help you think and learn.
🤖 Deep Learning uses “Artificial Neural Networks” (ANNs)—a bunch of connected math operations that act like neurons.
🔗 Each neuron in the network:
- Takes in information (like a picture of a cat 🐱)
- Makes a small decision about it
- Passes the info to the next neuron
The more neurons we have, the “deeper” the network is. That’s why we call it Deep Learning!
2. How Deep Learning Learns (Like a Kid!)
Imagine you’re a kid learning to recognize cats and dogs.
- You see a picture of a cat. 🐱
- Someone tells you, “That’s a cat!”
- You remember it. ✅
- Next time, you see another animal and guess…
- If you’re right → Your brain strengthens the memory!
- If you’re wrong → You learn from the mistake and try again.
Deep Learning works exactly the same way but much, much faster! 🚀
3. Why “Deep”? Layers of Learning!
Think of Deep Learning like a big sandwich 🥪, where each layer adds new knowledge:
- First Layer: Looks at basic features (lines, edges, colors)
- Middle Layers: Recognizes patterns (ears, eyes, tails)
- Final Layer: Understands the full picture (“Aha! It’s a cat!”)
The more layers, the smarter the AI becomes!
4. What Can Deep Learning Do?
Deep Learning helps with tons of cool things:
✅ Recognizing faces in photos 📸
✅ Understanding speech (like Alexa, Siri) 🎤
✅ Translating languages 🌍
✅ Playing games (like Chess & Go) 🎮
✅ Driving self-driving cars 🚗
That’s how AI can see, hear, and even talk like us! 🤖✨
Watch Video Lecture
Lecture 2: Deep Sequence Modeling
May 6, 2024
Recurrent Neural Networks, Transformers, and Attention
Alright! Imagine you’re in a classroom with a really smart robot teacher that helps you remember and understand things.
1. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) – The Storyteller
Think of RNNs like a storyteller who remembers the previous parts of a story while telling the next part.
📖 Imagine you’re reading a storybook one page at a time.
- To understand the current page, you need to remember what happened on the previous pages.
- RNNs work the same way—they remember past words when predicting the next one.
But there’s a problem! 😟
- If the story is too long, the robot forgets the beginning. (Like when you forget what happened in Chapter 1 of a long book!)
2. Transformers – The Super Smart Librarian
Since RNNs forget things, Transformers were invented to read the whole book at once instead of page by page!
📚 Imagine you have a librarian who doesn’t just read a book page by page but instead:
- Opens the whole book at once
- Finds the most important parts instantly
- Uses those parts to understand the story better
This means Transformers don’t forget things easily! That’s why they power tools like ChatGPT, Google Translate, and Siri!
3. Attention – The Magic Highlighter
Now, how does the librarian (Transformer) know which parts of the book are important?
🖍 Think of Attention like a magic highlighter ✨
- Instead of reading everything equally, the librarian highlights the most important words.
- For example, if the sentence is:
👉 “I went to the zoo and saw a lion.”- The most important word for “What animal did I see?” is “lion”
- Attention helps the Transformer focus on “lion” and ignore unnecessary words!
And that’s how modern AI understands language! 🤖🚀
Watch Video Lecture
Lecture 3: Intro to TensorFlow - Music Generation
MIT 6.S191 Lab 1: Intro to Deep Learning in Python and Music Generation with RNNs
Part 1: Intro to Deep Learning in Python – TensorFlow and PyTorch
TensorFlow (“TF”) and PyTorch (“PT”) are software libraries used in machine learning. Here we’ll learn how computations are represented and how to define simple neural networks in TensorFlow and PyTorch. The TensorFlow labs will be prefixed by TF; PyTorch labs will be prefixed by PT.
TensorFlow uses a high-level API called Keras that provides a powerful, intuitive framework for building and training deep learning models. In the TensorFlow Intro (TF_Part1_Intro) you will learn the basics of computations in TensorFlow, the Keras API, and TensorFlow 2.0’s imperative execution style.
PyTorch is a popular deep learning library known for its flexibility, ease of use, and dynamic execution. In the PyTorch Intro (PT_Part1_Intro) you will learn the basics of computations in PyTorch and how to define neural networks using either the sequential API and torch.nn.Module.
Part 2: Music Generation with RNNs
In the second portion of the lab, we will play around with building a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for music generation. We will be using a “character RNN” to predict the next character of sheet music in ABC notation. Finally, we will sample from this model to generate a brand new music file that has never been heard before!
Lecture 4: Deep Computer Vision
May 13, 2024
Watch Video Lecture
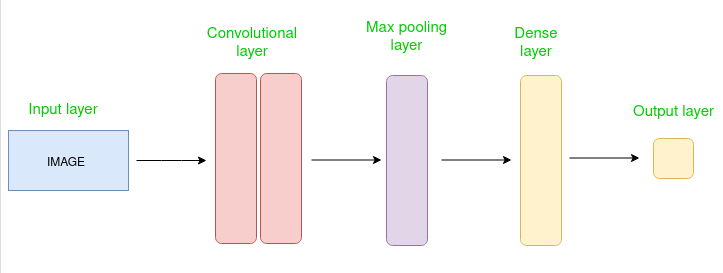
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) – The AI That Sees! 👀🤖
Imagine you have a robot friend 🦾 that wants to see and understand pictures—like recognizing cats, dogs, or even your face in a selfie!
That’s what Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) do! They are super smart at looking at images, just like our eyes and brain.
 —
—
1. Why Do We Need CNNs?
Regular neural networks struggle with images because pictures have millions of pixels! 😵
👀 Example:
A small image (100x100 pixels) has 10,000 pixels!
- A normal neural network would treat each pixel separately (very slow! 🐢).
- A CNN is smarter—it looks for patterns like edges, shapes, and textures, just like how humans recognize things!
2. How CNNs Work (Like a Detective!) 🔍
Step 1: Convolution – Finding Features
Think of CNNs like a detective with a magnifying glass 🔎.
- It scans small parts of an image piece by piece instead of looking at everything at once.
- It finds edges, curves, and colors (like eyes, noses, or ears in a face).
🔲 Example: If you’re looking for a cat 🐱, CNN first finds:
✔ Whiskers
✔ Ears
✔ Round face
Each part helps build the full picture!
Step 2: Pooling – Making It Simpler
CNNs then shrink the image while keeping important details.
- This makes processing faster and removes unnecessary noise.
- Think of it like zooming out on a blurry photo but still knowing it’s a cat! 🖼️
Step 3: Fully Connected Layer – The Final Guess!
After finding all features, CNN connects the dots and makes a final decision.
🧠 Example:
- “Does this image have whiskers? ✅”
- “Pointy ears? ✅”
- “A cute nose? ✅”
👉 It must be a cat! 🐱
3. What Can CNNs Do? 🤯
CNNs are used in tons of cool applications:
✅ Face Recognition – Unlock your phone with Face ID 📸
✅ Self-Driving Cars – Detecting traffic signs & pedestrians 🚗
✅ Medical Diagnosis – Identifying diseases in X-rays & MRIs 🏥
✅ Security Cameras – Detecting suspicious activity 🚨
Lecture 5: Deep Generative Modeling
May 20, 2024
Watch Video Lecture
Deep Generative Modeling – The AI That Creates! 🎨🤖
Imagine you have a magic artist robot 🦾🎨 that can create new pictures, music, or even human faces—things that never existed before!
That’s what Deep Generative Models do. They learn patterns from real data and then generate new, similar data—just like how a human artist learns to paint by studying other paintings.
1. What Does “Generative” Mean?
🔹 “Generative” means AI can create new things instead of just recognizing them.
🔹 Instead of just looking at cat pictures 🐱 and saying “This is a cat,” it can actually generate a brand-new cat picture that has never been seen before!
2. Types of Generative Models
There are two main types of Deep Generative Models:
1️⃣ Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) – The Artist & The Critic 🎭
Think of GANs like a game between:
🎨 An Artist (Generator) – Tries to create fake images.
👀 A Critic (Discriminator) – Tries to catch fake images and say, “Nope, that’s not real!”
🤖 How It Works:
- The Artist (Generator) starts by making bad drawings (random noise 🎨).
- The Critic (Discriminator) checks if they look real.
- If the drawing is bad, the artist improves. If it’s good, the critic gets tricked! 😲
- This battle repeats thousands of times until the Artist creates images that look real!
✅ GANs are used for:
- Creating realistic human faces (like deepfake videos 🎭)
- Making new paintings in the style of famous artists 🎨
- Enhancing old photos (turning blurry images into HD)
2️⃣ Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) – The Smart Copy Machine 📄🤖
A VAE is like a super-smart copy machine that:
- Learns to understand what an image looks like.
- Creates a slightly different version from scratch.
🤖 Example:
- It studies hundreds of dog pictures 🐶
- Then, it can imagine a new dog that doesn’t exist in real life!
✅ VAEs are used for:
- Generating new designs & sketches
- Creating new human faces or fashion models
- Generating synthetic medical data (for privacy-friendly AI training)
3. What Can Deep Generative Models Do? 🤯
Deep Generative Models are everywhere:
✅ AI Art – Creates beautiful paintings 🎨
✅ Deepfake Videos – Makes people say things they never said 🎭
✅ Text-to-Image Models – Like DALL·E (turns words into pictures 🖼️)
✅ AI Music – Composes original songs 🎵
✅ Medical Image Generation – Generates fake X-rays for research 🏥
Now, AI isn’t just thinking—it’s creating! 🎨🤖🚀
Lecture 6: Facial Detection Systems
Facial Detection Systems Research Paper, Code
Lecture 7: Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 27, 2024
Watch Video Lecture
Deep Reinforcement Learning – The AI That Learns by Playing! 🎮🤖
Imagine you have a robot student 🤖📚 that wants to learn how to play a game, drive a car, or even walk like a human.
Instead of just memorizing answers, it learns by trying, making mistakes, and improving—just like how you learned to ride a bike 🚴♂️!
That’s Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)!
1. What is Reinforcement Learning?
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is like teaching a dog tricks 🐶🎾.
1️⃣ You give it a command (“Sit!”)
2️⃣ If it sits correctly, you give it a treat 🍖 (reward ✅)
3️⃣ If it doesn’t, you give no treat ❌
4️⃣ Over time, the dog learns what gets rewards and what doesn’t!
Deep RL does the same thing but with a computer brain (AI)!
2. The Key Players in Reinforcement Learning 🎭
Every RL system has 3 main parts:
1️⃣ The Agent (The Learner) 🤖
This is the AI that is trying to learn—like a robot playing a video game.
2️⃣ The Environment (The World) 🌍
This is the place where the agent learns, like a game world, a self-driving car simulation, or a chessboard.
3️⃣ Rewards (The Prize 🏆)
The AI gets a reward for making good decisions and a penalty for making bad ones.
🤖 Example:
- If a self-driving car stays in the lane → ✅ Reward!
- If it crashes into a tree → ❌ Penalty!
Over time, the AI figures out how to win by choosing actions that give the best rewards!
3. How Deep Reinforcement Learning Works 🧠💡
Regular RL is too slow for complex problems (like playing chess or driving a car). That’s why we add Deep Learning to make it smarter!
🔹 Instead of guessing randomly, Deep RL uses Neural Networks to:
1️⃣ Remember past experiences 📚
2️⃣ Predict the best moves in the future 🔮
3️⃣ Improve itself over time ⏳
4. Cool Applications of Deep RL 🚀
🔥 AI Playing Video Games 🎮 – AlphaGo, DeepMind’s AI, defeated the world champion in Go!
🚗 Self-Driving Cars 🚘 – Learning to drive by practicing in simulations.
🤖 Robots Learning to Walk 🚶 – Teaching AI to move like humans!
📊 Stock Market Trading 📈 – AI learns to invest money smartly.
5. Summary
🔹 Deep RL is like training a dog – good actions get rewards, bad actions get penalties.
🔹 It has an Agent (Learner), an Environment (World), and Rewards (Prizes).
🔹 Deep Learning helps it learn faster and better!
🔹 Used in video games, self-driving cars, robotics, and finance!
Deep RL teaches AI to learn from experience—just like humans do! 🤖🎮🚀
Lecture 8: Language Models and New Frontiers
June 3, 2024
Language models are AI systems trained to understand and generate human-like text. Traditional models, like RNNs, struggled with long-term memory, but Transformers revolutionized NLP with self-attention mechanisms, leading to breakthroughs like GPT and BERT. These models power chatbots, translation tools, and content generation. The frontier is expanding with multimodal AI (text + images + speech), retrieval-augmented models, and AI agents that reason and plan. Ethical concerns around bias, misinformation, and AI alignment remain critical as we push toward more advanced, human-like intelligence. 🚀
Watch Lecture online
Lecture 9: Generative AI for Media
June 10, 2024
Lecturer: Doug Eck (Google). Douglas Eck is a Senior Research Director at Google, and leads research efforts at Google DeepMind in Generative Media, including image, video, 3D, music, and audio generation.
Lecture 10: Stories from Models in the Wild
June 17, 2024
Endless Experimentation: Building AI Models in the Wild. Lecturer: Niko Laskaris (VP, Customer Engineering) and Doug Blank (Head of Research) Comet ML





